Set out on an awe-inspiring travel through the universe with our extreme direct to understanding stars. These glowing firmament bodies, scattered over the night sky, are not fair lovely focuses of light but key players in the universe’s fantastic account. From the astonishing brilliance of our Sun to removed, puzzling stars in far-off systems, stars are essential to the infinite expressive dance. Our direct will enlighten the riddles of star arrangement, sorts, and their intriguing life cycles. Whether you’re an beginner stargazer or a prepared space expert, find the insider facts that make stars genuinely momentous and fundamental to our understanding of the universe.
What Are Stars?
- At its center, a star is a gigantic, brilliant circle of plasma held together by its possess gravity. Stars produce light and warm through atomic combination in their centers, where hydrogen iotas combine to frame helium, discharging colossal sums of vitality. This prepare makes stars sparkle brightly and permits them to be unmistakable from extraordinary distances.
The Arrangement of Stars
- Stars start their travel in tremendous clouds of gas and tidy known as nebulae. These clouds are fundamentally composed of hydrogen and helium, with little sums of heavier components. Beneath the impact of gravity, locales inside these clouds begin to collapse and condense. As the fabric accumulates, the center gets to be progressively hot and thick, in the long run coming to temperatures adequate for atomic combination to begin.
Protostar Stage

- Before a star completely shapes, it exists as a protostar. Amid this stage, the center proceeds to collect mass and warm, and the encompassing fabric shapes a turning disk. The protostar stage can final millions of a long time, amid which the question is not however obvious as a star.
Main Grouping Star

- Once atomic combination touches off in the center, the protostar gets to be a fundamental grouping star. This is the most steady and longest stage of a star’s life, where it remains for the lion’s share of its presence. The star wires hydrogen into helium, creating the vitality that makes it shine.
Types of Stars

- Stars come in different sorts, each with interesting characteristics. Understanding these sorts makes a difference us superior get a handle on the differences of stars in the universe.
Red Dwarfs

- Red diminutive people are the most common sort of star in the universe. They are little, cool stars with a moderately moo mass. In spite of their wealth, ruddy midgets are not effectively unmistakable to the exposed eye from Soil due to their faintness.
Main Grouping Stars

- Main arrangement stars change in estimate, temperature, and brightness. They incorporate stars like our Sun, which is a G-type fundamental grouping star. These stars are classified based on their temperature and glow, extending from hot, blue stars to cooler, ruddy ones.
Giants and Supergiants

- As stars age, they can grow and cool, getting to be mammoths or supergiants. These stars have expansive breadths and are regularly much brighter than their fundamental grouping partners. Ruddy mammoths, for occasion, are stars that have depleted the hydrogen in their centers and are in the handle of burning heavier elements.
White Dwarfs

- When a star depletes its atomic fuel, it may conclusion its life as a white overshadow. White diminutive people are hot, thick remainders of stars that have shed their external layers. They continuously cool and blur over time.
Neutron Stars and Dark Holes
- The most extraordinary leftovers of enormous stars are neutron stars and dark gaps. Neutron stars are inconceivably thick and little, composed primarily of neutrons. Dark gaps, on the other hand, have such solid gravitational pulls that not indeed light can elude them. These are the last stages of the most enormous stars’ lives.
The Life Cycle of Stars
- A star’s life cycle is a intriguing travel that ranges millions to billions of a long time. Here’s a closer see at how stars evolve.
Stellar Nursery: Nebula

- Stars start their lives in nebulae, where the conditions are idealize for the arrangement of modern stars. This stage can final from a few hundred thousand to a few million years.
Main Sequence

- During the primary arrangement stage, stars like our Sun stay steady and burn hydrogen into helium. This stage can final from a few billion a long time for littler stars to fair a few million a long time for the biggest ones.
Red Monster Phase

- As stars debilitate their hydrogen fuel, they extend into ruddy mammoths. This stage includes the combination of helium and other heavier components. Ruddy mammoths inevitably shed their external layers, taking off behind a thick core.
End Stages: White Predominate, Neutron Star, or Dark Hole
- The last stages of a star’s life depend on its mass. Littler stars ended up white diminutive people, whereas more gigantic stars may ended up neutron stars or dark holes.
The Significance of Stars

- Stars are significant to the universe for a few reasons. They are the essential sources of light and warm, impacting the tenability of planets. They moreover play a key part in the blend of components through atomic combination, contributing to the arrangement of planets and life.
Stars and Planetary Systems

- Stars are the centers of planetary frameworks. Planets circle stars due to their gravitational drag. The characteristics of a star, such as its mass and temperature, influence the sorts of planets that can shape around it.
Stellar Nucleosynthesis
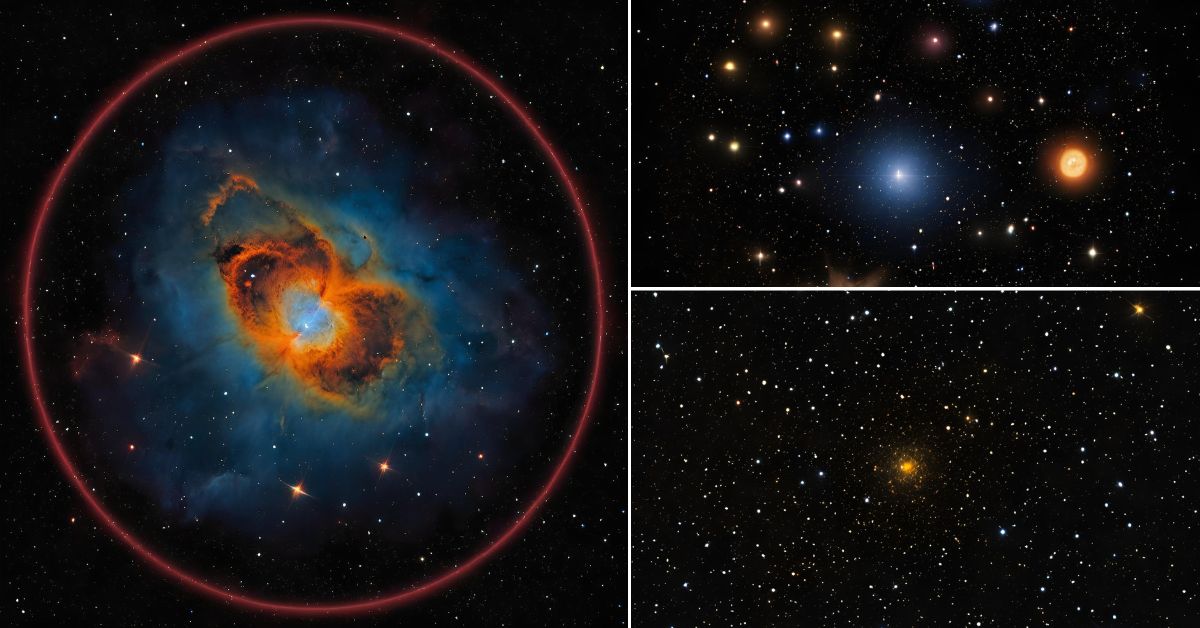

- Stars are capable for making most of the components found in the universe through a handle called stellar nucleosynthesis. Heavier components like carbon, oxygen, and press are manufactured in the centers of stars and dispersed into space when they die.
Light from Stars

- The light we see from stars can tell us a part around their composition, temperature, and separate. By considering this light, space experts can learn around the physical properties of stars and their part in the universe.
Observing Stars

- Observing stars can be both a leisure activity and a logical endeavor. There are different apparatuses and strategies utilized to ponder stars, from telescopes to space missions.
Telescopes

- Telescopes are fundamental for watching removed stars. They can be ground-based or space-based, with each sort advertising special focal points. Ground-based telescopes are constrained by the Earth’s environment, whereas space telescopes dodge this issue and can watch in different wavelengths.
Space Missions

- Space missions, such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the James Webb Space Telescope, give point by point perceptions of stars and other ethereal objects. These missions offer assistance researchers assemble information on far off stars and their properties.
Fun Truths Approximately Stars
- Stars Are Born in Clusters: Most stars are born in clusters or maybe than in isolation.
- The Closest Star: The closest star to Soil, aside from the Sun, is Proxima Centauri, found almost 4.24 light-years away.
- Star Colors: The color of a star demonstrates its temperature, with blue stars being the most smoking and ruddy stars being the coolest.
The Material science of Stars
Understanding the material science behind stars includes examining their inner forms, from atomic combination to radiation transport. Here’s a closer see at these complex mechanisms:
Nuclear Fusion

- Nuclear combination is the prepare that powers stars. In their centers, stars combine hydrogen particles to shape helium. This prepare discharges vitality concurring to Einstein’s condition,
- 𝐸=𝑚𝑐2 E=mc2
- . As stars advance, they begin combining heavier components, like carbon and oxygen, once hydrogen is exhausted. This movement of combination responses impacts the star’s lifecycle and inevitable fate.
Energy Transport

- Stars transport vitality from their centers to their surfaces through radiation and convection. In the radiative zone, vitality moves outward by means of electromagnetic radiation, whereas in the convective zone, it is transported by convective streams. This instrument is vital for keeping up a star’s soundness and luminosity.
Stellar Airs and Spectroscopy
A star’s climate is composed of different layers, each with particular properties and temperature slopes. By considering the light from stars, researchers can learn around these layers.
Photosphere
- The photosphere is the obvious surface of a star, where the light is radiated. Its temperature ranges from around 3,000 K for ruddy stars to over 30,000 K for blue stars. The photosphere is not a strong surface but a layer where the thickness drops sufficient for light to escape.
Chromosphere and Corona
- Above the photosphere, the chromosphere and crown are less thick but more smoking layers. The chromosphere is known for its ruddy color amid sun oriented shrouds, whereas the crown is a diffuse, hot external climate expanding millions of kilometers into space.
Spectroscopy
- Spectroscopy includes analyzing the range of light transmitted by a star. By examining assimilation and outflow lines in a star’s range, researchers can decide its composition, temperature, thickness, and speed. This procedure has uncovered the nearness of components like hydrogen, helium, and metals in stellar atmospheres.
Stellar Advancement in Detail
- The prepare of stellar advancement shifts altogether depending on a star’s mass. Let’s investigate the stages of advancement for distinctive sorts of stars.
Low-Mass Stars
Low-mass stars (less than 2 sun oriented masses) take after a unsurprising path:
- Main Arrangement: They spend most of their lives melding hydrogen into helium.
- Red Mammoth: Once hydrogen in the center is depleted, they grow into ruddy monsters. Helium combination starts in the core.
- Planetary Cloud: The external layers are removed, shaping a planetary nebula.
- White Overshadow: The remaining center gets to be a white overshadow, continuously cooling and darkening over billions of years.
High-Mass Stars
High-mass stars (more prominent than 8 sun based masses) involvement a more sensational evolution:
- Main Grouping: They intertwine hydrogen quickly, burning brighter and more sultry than lower-mass stars.
- Supergiant: After debilitating hydrogen, they grow into supergiants. Heavier components are melded in the core.
- Supernova: When combination ceases, the center collapses, activating a supernova blast. This occasion scatters overwhelming components into space.
- Neutron Star or Dark Gap: The remainder center may ended up a neutron star or collapse into a dark gap, depending on its mass.
Stellar Populaces and Galactic Structure
Stars are categorized into diverse populaces based on their age, composition, and area inside the galaxy.
Population I Stars

- These are youthful, metal-rich stars found basically in the disk of the Smooth Way, counting our Sun. They are frequently found in star clusters and locales of dynamic star formation.
Population II Stars

- Older and metal-poor, these stars dwell in the galactic corona and globular clusters. They are leftovers of the early universe and give experiences into the early stages of galactic evolution.
Population III Stars

- These theoretical first-generation stars were composed nearly completely of hydrogen and helium. They are accepted to have shaped in the blink of an eye after the Enormous Blast and contributed to the enhancement of the early universe with heavier elements.
Star Clusters and Associations
Stars regularly frame in bunches, which can be classified into distinctive sorts based on their age and arrangement history.
Open Clusters
- Open clusters are bunches of youthful stars that shaped from the same atomic cloud. They are generally free and can contain hundreds to thousands of stars. Cases incorporate the Pleiades and the Hyades.
Globular Clusters
- Globular clusters are thick, round collections of more seasoned stars circling the galactic center. They contain hundreds of thousands of stars and are among the most seasoned objects in the galaxy.
Stellar Associations
- These are free bunches of youthful stars that share a common root but are not as firmly bound as open clusters. They regularly have tall speeds relative to the galactic plane.
The Affect of Stars on the Universe
Stars play a significant part in forming the universe in a few ways.
Chemical Enrichment
- Stars synthesize and disseminate overwhelming components through nucleosynthesis and supernova blasts. These components contribute to the arrangement of planets and life. For occurrence, components like press and silicon are vital for rough planets and life as we know it.
Galactic Dynamics
- Stars contribute to the elements and structure of systems. Their conveyance, movements, and intelligent impact the arrangement and advancement of galactic structures, such as winding arms and galactic halos.
Cosmic Evolution
- The life and passing of stars drive the infinite cycle of matter. Supernovae and stellar winds improve interstellar gas with overwhelming components, fueling the arrangement of modern stars and planetary systems.
Observational Methods and Advances
Advancements in innovation have upgraded our capacity to consider stars.
Radio Astronomy
- Radio telescopes identify outflows from stars and other firmament objects at radio wavelengths. This method has uncovered pulsars, which are quickly turning neutron stars emanating pillars of radiation.
Space Telescopes
- Space-based observatories, such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the James Webb Space Telescope, give clear sees of stars and systems past Earth’s climate. These perceptions offer assistance in examining the universe’s most punctual stars and removed galaxies.
Gravitational Wave Astronomy
- Gravitational waves are swells in spacetime caused by gigantic objects like consolidating dark gaps or neutron stars. Watching these waves gives experiences into stellar remainders and high-energy astrophysical events.
The Future of Stellar Research
As innovation advances, unused strategies and revelations will proceed to extend our information of stars. Key zones of future inquire about include:
- Exoplanetary Ponders: Exploring planets circling other stars to get it their arrangement and potential for life.
- Stellar Contribute: Utilizing helioseismology and asteroseismology to test the inner structures of stars.
- Stellar Populace Thinks about: Mapping the dissemination and characteristics of diverse stellar populaces over the universe.
By persistently progressing our observational and expository capabilities, we will develop our understanding of stars and their centrality in the cosmos.
READ MERO ABOUT: “What is a Starlink Satellite Train? Everything You Need to Know”
READ MERO ABOUT:“What is a Starlink Satellite Train? Everything You Need to Know”
FAQs
What do you know about celestial bodies?
- Ethereal bodies are wonderful objects in the universe, each with its claim one of a kind characteristics. They incorporate stars, planets, moons, comets, and space rocks, all of which contribute to the endless, perplexing embroidered artwork of our universe. Stars, like our Sun, are colossal circles of gleaming gas that create light and warm through atomic combination. Planets circle stars, with Soil being a prime case, facilitating assorted environments and life shapes. Moons go with planets, including to their charm. Comets and space rocks, composed of shake and ice, offer bits of knowledge into the early sun based framework. Investigating these firmament ponders extends our understanding of the universe and our put inside it.
What are the 8 celestial bodies?
- The eight firmament bodies in our sun oriented framework, each with its possess charm, are the Sun, Mercury, Venus, Soil, Defaces, Jupiter, Saturn, and Neptune. The Sun, a brilliant star, is the heart of our sun based framework, giving light and warmth. Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun, is known for its extraordinary temperatures. Venus, with its thick air, is a shining world of seriously warm. Soil, our domestic, gloats different life and scenes. Damages, the Ruddy Planet, captivates with its potential for past life. Jupiter, a gas monster, is famous for its Incredible Ruddy Spot. Saturn’s staggering rings are unmatched in excellence, and Neptune, the far off blue planet, is a world of secret. Each firmament body includes to the ponder of our infinite neighborhood.
What kind of celestial body is a star?
- A star is a mesmerizing firmament body, a gleaming circle of hot gas that produces its possess light and warm through atomic combination. At its center, a star wires hydrogen into helium, creating colossal vitality that emanates outward, making the light and warmth we see from Soil. Stars come in different sizes, colors, and stages of life, from the brilliant blue monsters to the unpretentious ruddy diminutive people. Each star is a energetic, ever-evolving substance, playing a vital part in the infinite expressive dance of the universe. Their brilliant magnificence and life-giving vitality make stars essential to the presence and advancement of worlds and planetary frameworks.
What is the basic knowledge of stars?
- Understanding the nuts and bolts of stars uncovers their significant excellence and noteworthiness. Stars are enormous circles of hot gas, essentially hydrogen and helium, experiencing atomic combination in their centers. This combination handle discharges colossal vitality, making the light and warm we watch. Stars shift in estimate, color, and life expectancy, extending from brilliant blue monsters to cooler ruddy diminutive people. Their life cycle incorporates stages such as fundamental grouping, ruddy mammoth, and, in the long run, supernova or white overshadow, depending on their mass. Stars are principal to the arrangement of systems and planetary frameworks, and their consider offers experiences into the universe’s past, display, and future.
What are 10 facts about stars?
- Composition: Stars are essentially made of hydrogen and helium, with atomic combination happening in their centers to create energy.
- Nuclear Combination: Stars produce light and warm through atomic combination, where hydrogen molecules combine to shape helium, discharging vitality in the process.
- Color and Temperature: The color of a star shows its temperature. Blue stars are the most smoking, whereas ruddy stars are cooler.
- Life Cycle: Stars go through a life cycle that incorporates stages like fundamental grouping, ruddy mammoth, and, depending on their mass, may conclusion as a white overshadow, neutron star, or dark hole.
- Size Varieties: Stars shift in estimate from little ruddy diminutive people to enormous supergiants. The biggest stars can be hundreds of times bigger than the Sun.
- Star Clusters: Stars regularly frame in clusters inside nebulae. Striking clusters incorporate the Pleiades and the Hercules Cluster.
- Binary Frameworks: Numerous stars are portion of double or different star frameworks, where two or more stars circle a common center of mass.
- Distance: The closest star to Soil, after the Sun, is Proxima Centauri, found around 4.24 light-years away.
- Brightness: A star’s brightness, or radiance, depends on its measure, temperature, and remove from Soil. It is measured in magnitudes.
- Star Arrangement: Stars are born from the gravitational collapse of gas and tidy in atomic clouds, driving to the arrangement of protostars that inevitably light combination.
Conclusion:
- Stars are the crucial building pieces of the universe, giving light, warm, and the components essential for life. Understanding stars includes investigating their arrangement, sorts, advancement, and affect on the universe. With continuous headways in observational innovation and hypothetical models, our information of stars proceeds to develop, advertising more profound experiences into the workings of the universe. “Stars: Everything You Require To Know” gives a comprehensive diagram of these firmament ponders, enlightening their part in forming the universe and our put inside it.

